Pneumatic device measurement for oil and gas
- Client Name
- Confidential
- Location
- New Mexico, Wyoming, Texas, USA

Challenge
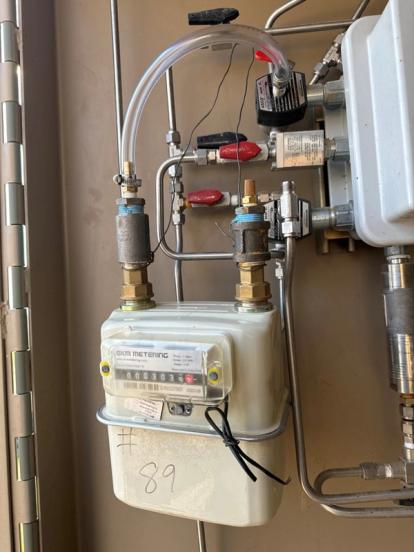
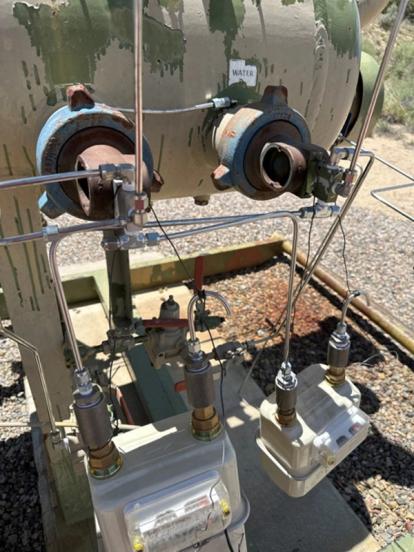
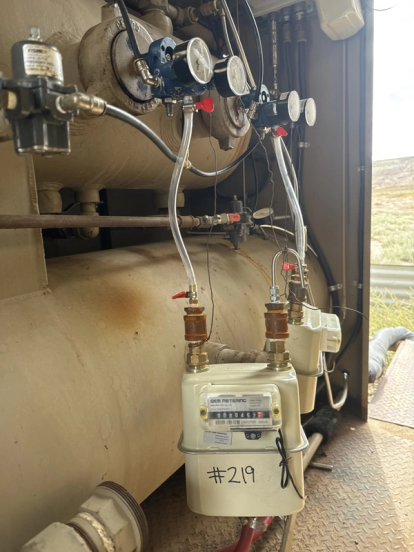
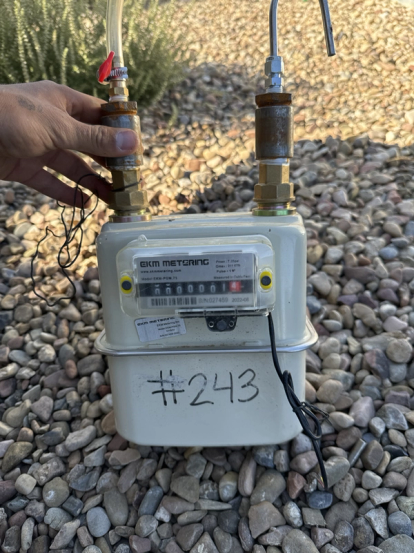
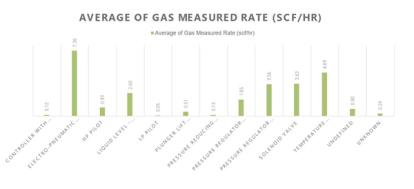
SLR was contracted to conduct a measurement study of gas-driven pneumatic controllers across three of the client’s oil and natural gas production regions in the lower 48 states: the San Juan Basin in northwest New Mexico, the Rocky Mountain Region in west-central Wyoming, and the Gulf Coast Region in East and South Texas. Using positive displacement meters temporarily installed on each controller, natural gas emissions were measured over 48-hour periods during routine venting. Nearly 2,500 controllers were measured across the three regions over a five to six-month period.
The study was originally intended to demonstrate that gas-driven pneumatic devices operating across the client’s regions emitted significantly less than EPA default emission estimates, with the goal of reducing their methane Waste Emissions Charge (WEC) fees. After the EPA revoked the methane WEC rule, the client shifted the project’s purpose to an internal study of existing gas-driven devices to determine their actual release rates. The results helped the client identify device groupings and types with consistently high release rates, as well as outliers with excessive emissions that could indicate malfunction and the need for replacement.
Solution
The client sought a contractor with expertise in methane measurement deployments who could also conduct an in-depth technical analysis and prepare a study of the results that would withstand scrutiny from state and federal regulators.
SLR is considered best-in-class for its technical and management expertise in methane emissions in the oil and gas industry. Its senior-level experts have led or participated in major published US field measurement and characterization studies and development of protocols and best practices in methane emissions from the oil & gas industry since the early 1990s.
SLR managed the project and provided ongoing technical and data management support. The team developed an ArcGIS field data app for data collection, set up a centralized database for uploading field data, performed data review and quality assurance, and prepared a detailed presentation comprising more than 80 slides that summarized the study and its results.
Impact
SLR engaged two subcontractors to provide field technicians responsible for installing, removing, and recording measurement data across the three operating regions. The study found that average whole gas measurements were less than half of the default USEPA emission factor of 8.8 scf/hour specified in 40 CFR 98, Subpart W (GHGRP), when anomalies, outlier events, and common point measurements were excluded.





